Volumio Architecture
Introduction
Volumio is essentially a custom made Operating System optimized for Music Playback, which performs operations thanks to a NODE.js backend, which can be accessed via various clients and interfaces. The main interface is Volumio's Web UI, which is built with Angular.
Components
Volumio OS
Volumio OS is a custom OS based on Debian (buster at the time of writing). It contains only the bare minimum utilities to get Volumio running, to be as lightweight as possible.
Source code can be found on Github at the Volumio 3 OS Repo
Volumio Core
Volumio Core or Backend is a serverside application (written in NODE.js) which runs the music player, music library, and other functions.
Volumio Core has an MVC-like architecture which breaks the player functionality into modules. The modules are organized by function: clients, interfaces, core, controllers, services, and output.
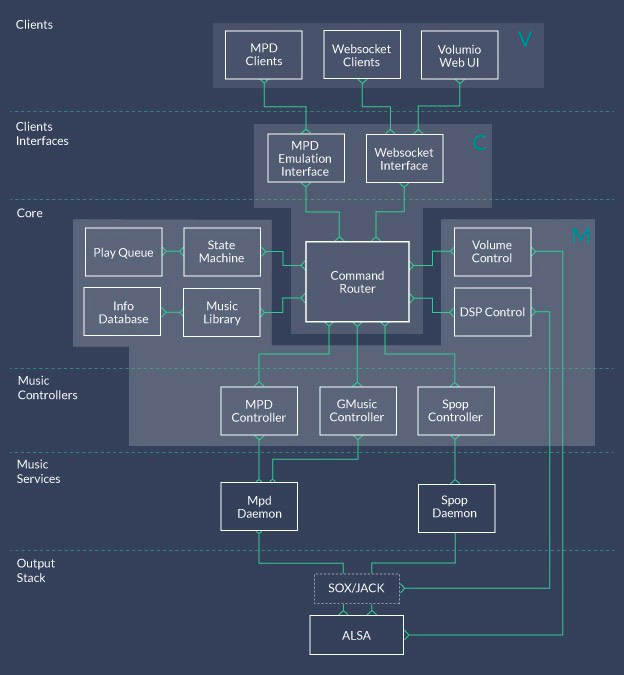
Clients
The clients represent anything that can open a connection with the Volumio server and send commands. This is code that runs on the client machine, whether it be a PC, tablet, phone, or watch. The Volumio WebUI is one of the possible clients you can use to connect to the Volumio server. It communicates to the server using a standard websocket protocol. And since this is a standard protocol, users may code any other web interface they want, and have it drive Volumio.
Interfaces
Which brings us to our next group of modules, the interfaces. Interfaces serve as the intermediaries between the clients and the Volumio core. They translate what are typically text commands into function calls that the core executes. These interface modules are designed to be interchangeable - they offer a set of standard methods that the core can call, and return data in a standard format. We are developing this standard as we go, but the general idea is that users can drop in their own interface modules, which will allow for more interface options than just websocket and MPD emulation. For example, one could write an interface module for hard controls (real knobs and buttons, imagine that!), for local kiosk-style control, etc.
Core Modules
The core modules run the logic behind the Volumio player. The state machine module contains logic for switching between player states like play, pause, and stop. The play-queue module maintains the list of tracks which are queued up to play. The play queue may contain tracks from any music service. The music library module (more about this later) maintains a database of all the tracks across all services that the user has active, and allows for browsing and searching. The device selector would allow a user to switch between different output sinks - this is yet to be coded, I'm still trying to figure out what this means! The volume module allows for hardware or software level control of the output volume. Finally, the command router module contains no logic, it merely routes function calls to the various other modules.
Music Services Plugins
The music controllers are modules which can communicate with individual music services or daemons. Each music service will have its own controller module. The controller can retrieve music information from the service or daemon, and can also send commands to control playback. It is important to note here that each music daemon likely has its own built-in play queue and playback status. The Volumio state machine keeps in sync with each of these separate play queues and statuses. This allows the user to interact with Volumio as if it were a single music player, and the Volumio Core controls each of the music services separately in the background. We are currently planning controllers for MPD, Spop, and possibly GMusic. We are also going to add a controller for Libgroove, a nice local audio renderer that can serve as an alternative to MPD. Libgroove uses libav for audio decoding (the same as what VLC uses). Each music controller module will be interchangeable like the user interface modules. Users can write controllers for new music services they would like to add.
Source code can be found on Github at the Volumio 3 Backend Repo
Frontend
The frontend is the integrated Web User Interface in Volumio. Currently there are 3 different UI Flavours of UI:
Classic UI, the first iteration of Volumio's User Interface Classic UI Source Code
Contemporary UI, a revised iteration of Volumio's User Interface Contemporary UI Source Code
Manifest UI, the latest and greatest Volumio experience. This Manifest UI source code is not available
Plugins
Plugins are an easy way to extend Volumio's functionality. For more informations see the Plugins Section